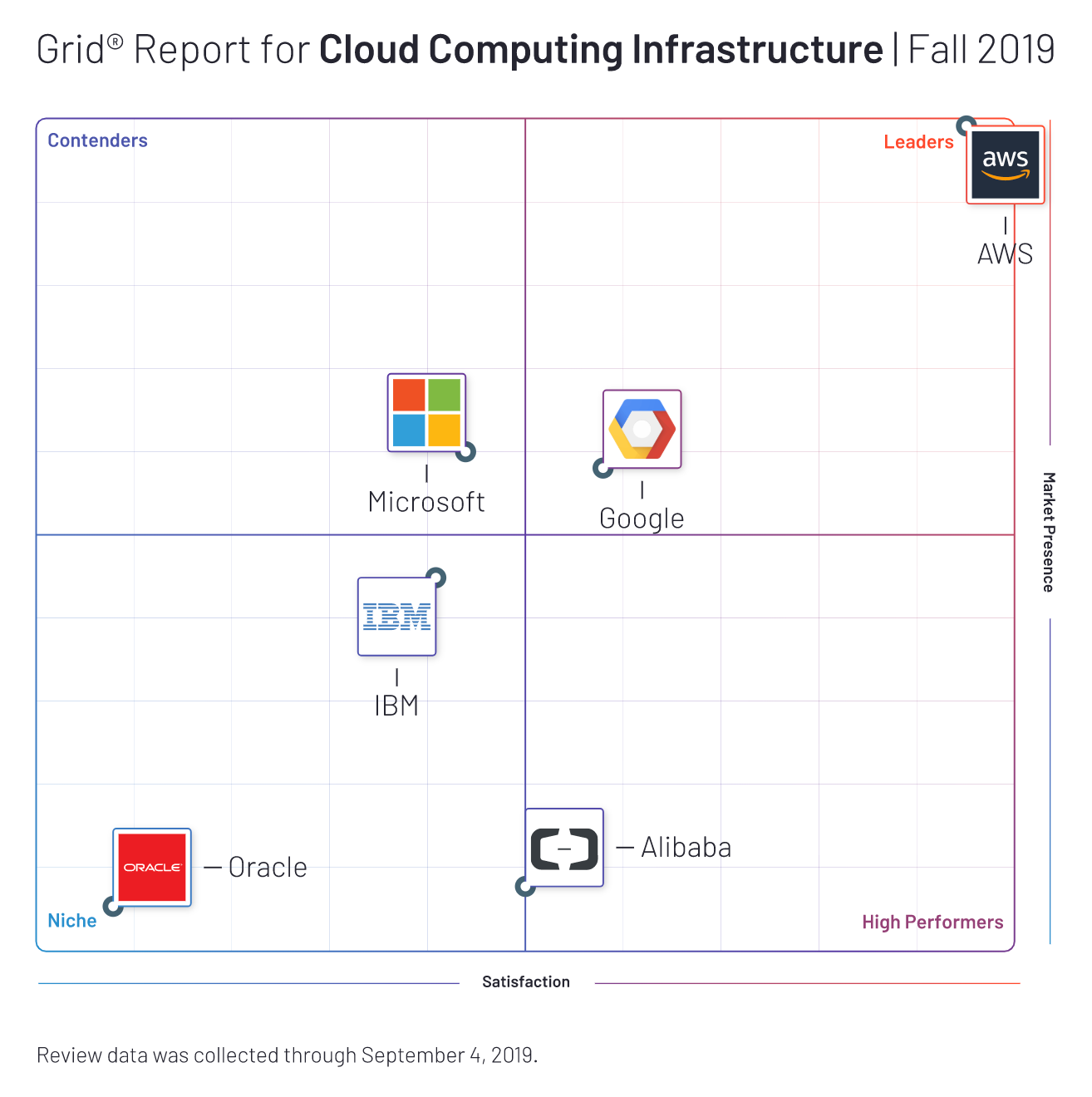
Fall 2019
Grid for Cloud Computing Infrastructure
Cloud Computing Infrastructure vendors offer the ability to host computing capacity in an elastic, scalable environment. Business can host their cloud computing publicly on servers owned and managed by third-party vendors, privately on a single-tenant server, or using a combination of both. These cloud computing services range from hosting infrastructure and databases in the cloud to cloud-based application development and hosting platforms, among many other services.
Cloud computing infrastructure providers offer an “as a service” subscription model, where the third-party vendor manages and administers the necessary backend services to help businesses easily scale and grow as necessary. This ensures companies do not need to worry about the availability of their development environment or their infrastructure—regardless of fluctuations in demand—and can instead focus on more business-critical functions.
Cloud computing is made up of disparate services and tools that can be utilized individually or combined to create a deeper cloud computing stack. The core categories that fall under Cloud Computing Infrastructure are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Cloud Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Database as a Service (DBaaS). Additionally, Cloud File Storage, Container Management, Container Orchestration, Container Registry, Hybrid Cloud Storage, Load Balancing, Object Storage, and Virtual Private Cloud solutions all fall under the umbrella of cloud computing infrastructure vendors.