In the contemporary business world, it is important for every business, whether they are a product or a service provider, to build their digital presence.
A digital presence gives businesses the platform to reach customers worldwide and builds their brand image among the buyer community.
For businesses to set up an online presence, they require the services of a web hosting provider.
However, hosting a website is only the tip of the iceberg. Hosting providers may offer robust functionalities that include hosting applications and digital stores, offering file storage and backup, security services, and much more.
What is web hosting?
Web hosting is a service in which the provider (or the web host) offers the functionality of hosting websites to its clients. They help clients create and maintain their websites and allow visitors to access their content on the internet.
When an organization opts for a web hosting plan, they rent space on a server for storing the website’s content.
Web hosts ensure that the server is functioning smoothly, and data such as images, texts, and other information are transferred to the visitors’ web browsers. They must also have security measures in place to safeguard the website.
Types of web hosting services and how G2 categorizes them
At G2, we identified the variety of hosting services available and launched five new subcategories of web hosting providers as well as an additional Cloud Hosting Providers category.
Web hosting is a broad concept. Previously on G2, under the Hosting parent category, there were three child categories: Web Hosting, Managed Hosting Providers, and Virtual Private Servers (VPS) Providers.
To better reflect the evolution in the web hosting space and help our buyer community make informed decisions, we converted the Web Hosting Providers category into a parent category and Managed Hosting Providers and Virtual Private Servers (VPS) Providers into its child categories.
Let us examine the purpose of each of these providers and how they can help organizations meet their hosting requirements.
The newly launched subcategories of web hosting
G2 launched five new child categories to better represent the web hosting space as follows:
1. Shared Hosting Providers: Under a shared hosting plan, the customer shares a single physical server and its resources with other websites. Since the resources are shared, the cost of this hosting plan is much lower as compared to other forms of web hosting.
If a website uses more than its ideal share of resources, the other users' website performance will be compromised. Also, if other sites that share their server get labeled as “spam,” it can have a negative impact on their SEO, and their email campaigns may land in junk folders until they buy a dedicated IP for their hosting plan.
Given its low cost and ease of use, this type of hosting plan is ideal for startups and small businesses.
2. Dedicated Hosting Providers: Dedicated hosting provides a private physical server(s) to a single customer. The organization leases the entire server, and has complete control over it. This allows them to configure and optimize the server as per their business requirements.
Dedicated hosting also offers high levels of security to the client. Given the amount of resources allocated for a single user, such as storage space, bandwidth, and more, it is one of the most expensive forms of web hosting.
This type of web hosting is suited for large organizations or websites with high traffic volume.
3. Colocation Hosting Providers: Colocation hosting is similar to dedicated hosting as it offers resources to scale the organization’s web resources and ensures high levels of security.
Under dedicated hosting plan, an organization leases the server. Colocation hosting, however, allows organizations to host their own servers in a third-party data center for a more secure and managed infrastructure.
Since the hardware or server is owned by the organization, colocation hosting also offers the flexibility of configuring and exercising complete control over their servers.
This type of hosting is ideal for mid-sized businesses and enterprises whose websites get a high volume of traffic. This may also be suited for small companies that do not have their own data centers.
4. Reseller Hosting Providers: Under a reseller hosting plan, a business can buy a web hosting plan from a provider, rebrand, and sell those services to other clients as their own. Reseller hosting packages are available at a standard wholesale rate.
Reseller plans allow users to sign up as a reliable host and sell the services to other clients at a markup. The reseller host can set their own pricing and conditions, provided they work within the web host’s conditions.
Reseller hosting is one of the least expensive forms of hosting that allow businesses to make profits easily.
This type of hosting is ideal for digital agencies or web developers who build client websites and offer hosting services for those websites.
5. WordPress Hosting Providers: Under a WordPress hosting plan, servers and resources are developed and made available for WordPress sites. However, it is not mandatory for organizations to specifically sign up for a WordPress hosting plan. WordPress can also be run on other types of hosting plans.
WordPress hosting is comparatively more expensive than a shared hosting plan as it offers features, functionalities, and services which are specific to WordPress. WordPress offers plugins and themes to simplify the installation of a WordPress website.
This type of hosting is for users who are willing to manage their websites through WordPress. Users can opt for managed or unmanaged WordPress hosting.
Managed WordPress hosting is ideal for organizations wanting to outsource their site maintenance, security, and responsibility of ensuring uptime to the hosting providers. Unmanaged WordPress hosting is best for organizations that want to create and manage their own websites.
Cloud hosting and its growing popularity
Cloud hosting providers is one of the latest additions to G2’s portfolio of hosting categories.
To understand cloud hosting better, let’s take the example of a birthday cake. While the cake is sliced up and divided among many children, each slice completely belongs to one child, and they do not need to share it with someone else.
Cloud hosting can offer multiple advantages and combined benefits of both shared and dedicated hosting services. It allows a virtual server to either be shared or dedicated to one organization. It is also lower in cost as opposed to dedicated hosting as it follows the pay-as-you-go model, allowing users the option of allocating the resources where required and paying only for the number of resources used.
Cloud hosting deploys servers in multiple locations around the world. It uses the platform as a service (PaaS) and infrastructure as a service (IaaS) models to store the data in different server locations. Users have the option of using bandwidth, storage, and other resources of these different servers.
Thus, the website and applications are available to users at a much higher speed. This also minimizes website downtime; if one server is down, another server can take its place and ensure visitors can access it.
What is the difference between web hosting and cloud hosting?
Unlike traditional web hosting that commonly deploys a physical server, cloud hosting uses a network of physical and virtual servers to host multiple sites. It is also used for delivering applications using cloud resources to users in different locations.
Cloud hosting allows its users the flexibility and ease to scale resources as demand increases. Under web hosting, the organization needs to upgrade their plan to keep the website up and running in case of a spike in web traffic.
The G2 data on the hosting categories
The graph below shows the percentage change in the total number of reviews to hosting categories on G2 since the month of their launch.
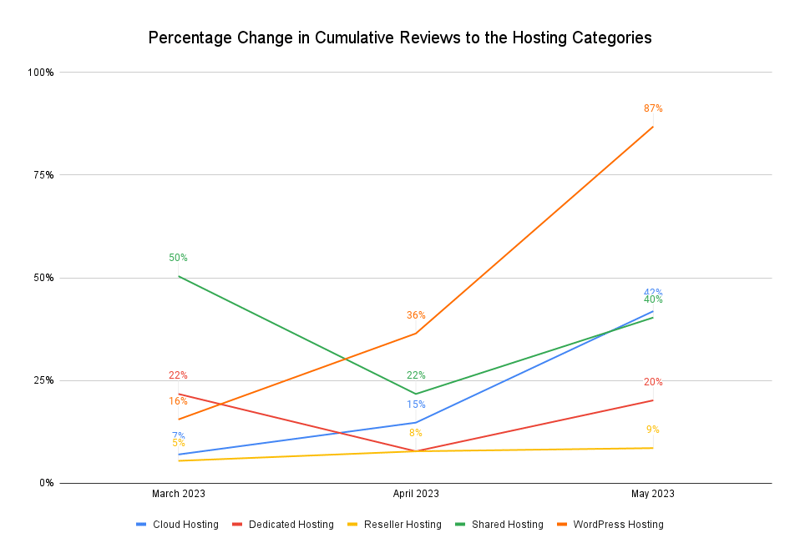
Source: G2 Reviews for Hosting Categories
For all the categories, barring colocation hosting providers, the review count has increased over the last few months. This shows that buyers are exploring the various types of hosting services to have a granular view of the hosting ecosystem and better differentiate and decide which type of service is best suited to their business needs.

Choosing the right type of hosting provider is the key
Hosting a website or web application on the internet is not the end of the story. It is equally important to ensure uptime so that the website or the application is available to visitors 24/7.
Depending on the primary business goal, budget, size of business, volume of traffic, security requirements, and various other factors, businesses need to decide what kind of hosting would be optimal for their needs. This would help them easily navigate the solutions and make the right selection.
Dive deep into the basics of VPS hosting and learn more about its types, benefits, and best practices to follow to make VPS hosting work for you.
Edited by Sinchana Mistry


 by Anindita Sengupta
by Anindita Sengupta
 by Anindita Sengupta
by Anindita Sengupta
 by Anindita Sengupta
by Anindita Sengupta