Planning production operations is the next step after resource management and probably the most important in manufacturing.
With a critical process like production planning, ERP software is invaluable for operational efficiency and strategic decision-making. Let’s examine some obstacles manufacturers face during production planning and explore how the right ERP solution helps tackle these challenges.
How to identify and address production planning challenges
Production planning defines how resources will be used on the shop floor, impacting manufacturing process results. Whether the finished products comply with quality standards and customer expectations depends on the accuracy of production planning.
Creating and implementing production plans can be complicated and requires special attention to the following.
1. Identify and focus on the details that matter most
While production cycles can be adjusted to compensate for minor details, the major ones may completely compromise the finished products.
For instance, a food and beverage manufacturer may alter the color or flavor of its products during production but won't be able to reverse the fermentation process for beverages. Therefore, getting the fermentation right the first time is critical. This requires detailed planning of the ingredients needed, the recipe to combine them, the equipment to use, and the conditions (temperature, humidity).
2. Take into account any waste
Waste is unavoidable. Even small amounts of waste per product will accumulate over time, and their cost needs to be included in the product's price. It is, therefore, preferable to plan for a certain percentage of wastage, then track the actual amount of waste and calculate the difference. Ideally, the difference should be as close to zero as possible.
Cutting fabric or leather will always cause waste for a fashion and apparel manufacturer. While it's impossible to eliminate it, waste can be reduced by planning to cut similar patterns that maximize the use of raw materials.
3. Define workflows
Based on industry best practices and quality standards, it is essential to define workflows to implement operations in a logical sequence. In most cases, manufacturing operations follow a predefined order which cannot be easily changed. The more complex the industry, the more difficult it is to adjust production planning.
In a sector like aerospace and defense, making changes to production planning is much more complicated than in discrete manufacturing, like furniture. Imagine trying to make changes to the production of a plane versus tables and chairs.
How ERP software helps with production planning success
It is hard to imagine that anyone could achieve the above without using software. That being said, not any software fits the bill.
ERP was designed to help manufacturers prepare for most production scenarios. The most flexible ERP solutions also allow users to change features and workflows to adapt to the unpredictable situations described above.
Flexibility can be a double-edged sword since too much of it may create confusion on the shop floor. Manufacturers need software that provides standard workflows for production, which can only be customized by users with special access rights, such as production managers.
ERP software and centralized data
ERP helps manufacturers with centralized data on what needs to be manufactured, when, and how. Having accurate data is essential for production planning. Manufacturers rely on historical data to plan future production activities and to optimize planning.
In the fashion and apparel example above, using cutting patterns is the best way to reduce waste. These patterns are designed using software tools like computer-aided design (CAD) or sketching solutions. The data from these tools needs to be fed into the ERP solution, while the production data can also be used in CAD to improve patterns.
ERP software and process automation
Process automation provides visibility into operations and data across the company and its supply chain. It is common for manufacturers to create production plans without having the necessary raw materials in inventory. Also, specific production steps may be performed by partners in various geographical locations.
In the apparel industry, a company may buy fabric, send it out to a partner for dyeing, and then use it to cut and make the final product. These steps must be synchronized to reduce downtimes and logistics costs such as storage and transportation.
Depending on the industry and company size, various ERP functionalities, such as inventory and cross-location visibility, can be essential for production planning.
The table below shows some ERP software features that helped G2 reviewers from multiple industries.
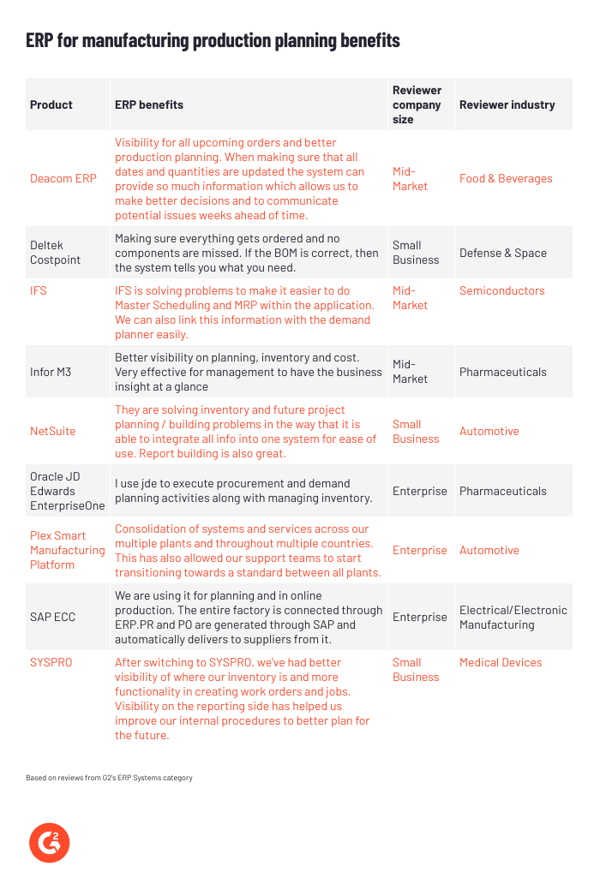
Despite significant challenges, production planning can be successful if manufacturers use robust ERP solutions that are flexible enough to adapt to their specific needs.
Production dispatching or the road of (almost) no return
ERP software is fundamental in production planning. It is strategically vital for companies to embrace this tool to overcome production challenges, promote efficiency, and streamline operations.
My next blog will describe how production plans are dispatched and executed on the shop floor. This step leaves little room for error, as resources, plans, and workflows should be set in stone before it starts. While exceptions exist, most ERP solutions can handle them with human supervision.
Optimize your business strategy with clarity. ERP vs. CRM: understand which is the right solution for your business.
Edited by Shanti S Nair

 by Gabriel Gheorghiu
by Gabriel Gheorghiu
 by Gabriel Gheorghiu
by Gabriel Gheorghiu
 by Gabriel Gheorghiu
by Gabriel Gheorghiu