This post is part of G2's 2024 technology trends series. Read more about G2’s perspective on digital transformation trends in an introduction from Chris Voce, VP, market research, and additional coverage on trends identified by G2’s analysts.
Consolidation of security investments in 2024
Prediction
Economic factors and increasingly innovative threat actor tactics will drive optimization and consolidation of security investments in 2024.
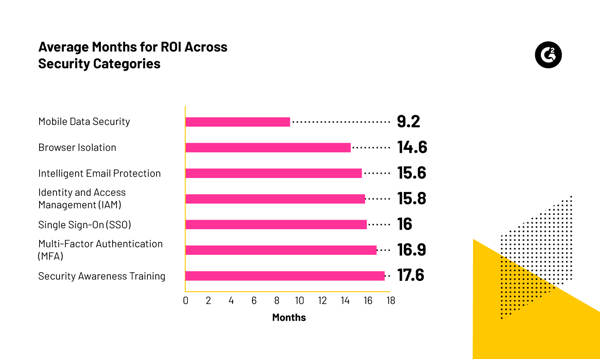
The return on investment (ROI) time for cybersecurity technology is a critical metric for businesses and organizations to consider. A shorter ROI time means that the technology can swiftly provide tangible value against the invested cost. This ensures that resources are not locked up in long-term, uncertain projects while threats continue to emerge.
The speed at which cybersecurity measures can effectively defend, detect, and mitigate threats becomes paramount as threat actors continue to evolve their tactics and leverage commoditized attack techniques.
Misconfiguration and unpatched vulnerabilities
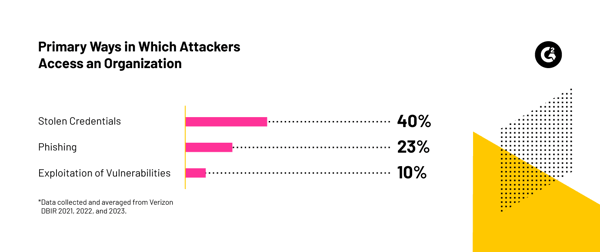
Misconfiguration and unpatched vulnerabilities remain persistent issues, with the Verizon 2022 and 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report stating that misconfigurations were the second most common cause of data breaches.
Given this, organizations must robustly manage and monitor their digital assets to prevent exploitable vulnerabilities. A systematic approach of regular patch management, security audits, and employing automated tools to monitor and correct misconfigurations is crucial to fortifying security posture as we move toward 2024.
IoT devices security: expansion of IoT devices
Statista reports that the global IoT connected devices are expected to surpass 75 billion by 2025, expanding the battlefield for cybersecurity. The massive proliferation of these devices symbolizes a significant security risk as they frequently lack robust built-in security.
A prudent approach involves proactive security integration into IoT devices’ developmental phase, regular firmware updates, and a strict selection process prioritizing the highest security standards.
Small and mid-sized business exploitation
Small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs), along with third parties, have historically been channels for cybercriminals to infiltrate larger organizations.
The 2013 Target data breach serves as a prime example, where cybercriminals hacked into Target’s system via an HVAC vendor, leading to the exposure of 40 million credit and debit card numbers.
In 2023, Cybersource reported that SMBs accounted for 28% of cyberattacks, underscoring the vulnerability of smaller entities and their role in the larger cybersecurity ecosystem. For larger enterprises, rigorous assessment and monitoring of the security postures of their third-party vendors and SMB partners is essential to close off this avenue of exploitation.
Reevaluating phishing and security awareness training
A report from Proofpoint's State of the Phish highlights that nearly 50% of organizations deal with at least one successful phishing attack. Despite substantial investments in training, phishing remains a significant threat.
In 2024, companies should reevaluate their expenditure on phishing and security awareness training. Considering investments in technologies like remote browser isolation (RBI) can substantially mitigate the risk by isolating malicious content from the user’s environment, ensuring seamless and secure browsing.
Future of cybersecurity: what to expect in 2024
In summary, anticipating and preempting the future threats is fundamental in navigating the cybersecurity terrain in 2024. Individuals and organizations must act by investing not just in advanced, AI/ML-integrated security solutions, but also by enhancing legal and regulatory compliance, focusing on IoT and remote work security.
Suggested technologies for investment include next-generation firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and zero trust capable platforms. A proactive, informed approach to cybersecurity will be the cornerstone in defending against the evolving cyber threats in the approach to 2024, ensuring the security and integrity of global digital ecosystems.
In an attempt to differentiate, cybersecurity vendors create distracting shiny objects. Learn more about the shiny object syndrome in cybersecurity.


 by Dr. Chase Cunningham
by Dr. Chase Cunningham
 by Dr. Chase Cunningham
by Dr. Chase Cunningham
 by Dr. Chase Cunningham
by Dr. Chase Cunningham