Generative AI is an artificial intelligence technology that can produce various types of content like text, imagery, audio, and synthetic data.
Consumers and companies are buzzing about AI-powered tools like ChatGPT and Bard that can generate human-like text based on writing prompts or past conversations.
However, security experts and vendors warn users about the exposure of valuable data like private customer data, a company’s classified information, or company trade secrets fed into these tools, where potential hackers can store, access, or misuse the data.
The undeniable growing popularity of generative AI tools
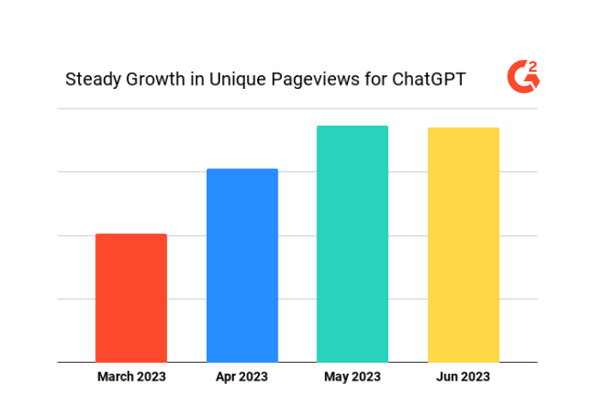
G2 data show that generative AI vendors such as ChatGPT are showing increased interest (in this case, unique page views) on G2.com. This reflects the growing interest, and possible use, of generative AI vendors, validating the attention to security concerns of generative AI.
The security challenges of using generative AI
The following are examples of increased security risks caused by using generative AI.
Increased risk of data breaches and identity theft
These generative AI tools often require writing prompts. When users share personal or corporate information with these generative AI tools, they may share more than they think.
The tools themselves fetch user data to construct the context. The lack of proper procedures for collecting data is of great concern to security experts.
Poor security in the AI tool
The addition of any new app into a corporate environment creates security concerns. Generative AI tools pose unique risks because they contain complex algorithms that make it difficult for developers to identify security flaws.
For example, a generative AI tool could be tricked into classifying dangerous malware as safe. A hacker can take strings from a non-malicious file and append it to a malicious one, tricking the generative AI into thinking it’s safe.
Poor development process
Companies can use generative AI applications for software development, but the usual controls for software development and lifecycle management, like accountability and security, may be absent.
Using generative AI applications for such purposes may risk the user’s privacy and security.
Deepfakes or hallucinations
As voice and facial recognition are used more for security authentication, it’s important to note that AI is an opportunity for hackers to create deepfakes to get unauthorized access.
The concern about data produced by generative AI is that it will create "hallucinations" that produce untruths.
How to prevent generative AI security issues
The following are tips on how to help prevent generative AI security issues within your organization.
- Compare tools: Evaluate a generative AI tool’s reputation versus its competitors. G2 has a Generative AI Software category you can explore.
- Review policies: Review your organization’s privacy and security policies before investing in generative AI tools. Make sure that these tools align with corporate policies, especially if your organization is in a highly data-sensitive industry.
- Consider new policies: Create new policies and training for your organization regarding using generative AI tools. For example, train employees on what data they can and cannot submit to such tools.
Future of generative AI and security
With the growing popularity of generative AI tools, so will the security risks. The best way for organizations to mitigate these risks is to proactively be aware of the tools used within the organization and how employees use them.
As AI hackers become more insatiable, ensuring your security tools, such as application security, are up-to-date and endpoint, password, and antivirus protection is crucial.
Learn how sharing information with ChatGPT creates privacy risks.
Edited by Shanti S Nair


 by Sarah Wallace
by Sarah Wallace
 by Sarah Wallace
by Sarah Wallace
 by Sarah Wallace
by Sarah Wallace