Data management is complex and vast.
Every piece of data comes with its metadata, which is essentially data that describes other data. Metadata management is an integral part of data governance and is essential for maintaining historical records of long-term data sets and ensuring their longevity.
Proactive data management with active metadata
Metadata is additional information describing data information that provides context about data assets in any organization. Metadata helps in data management by locating and accessing required data by providing information about the datasets' location, content, and format.
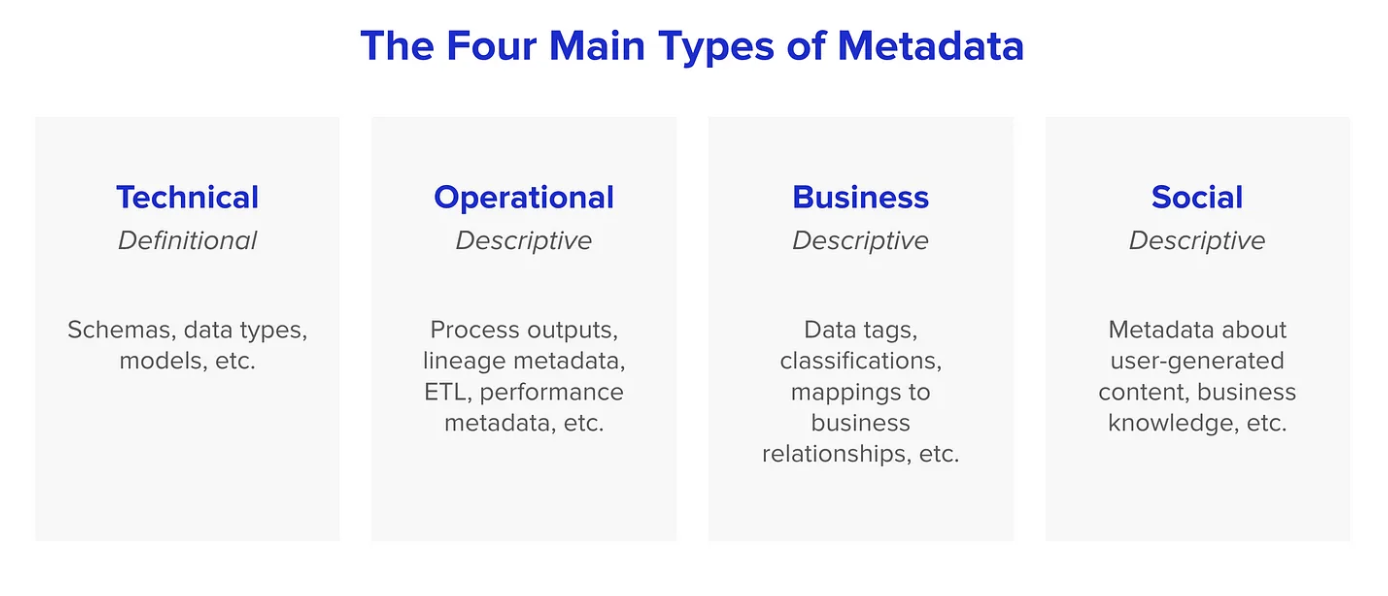
Source: Towards Data Science
Metadata management has always been a static human-in-a-loop strategy that uses algorithms.
What is active metadata?
Active metadata changes by itself as the data changes. The metadata continuously gets generated, collected, and indexed when the data gets used, modified, or generated.
Initially, metadata was used only as information about the data profile. Active metadata now manages data access, data classification, and data quality.
Transitioning to active metadata from traditional data catalogs
We know of two types of metadata based on its functionality: active and passive.
Passive metadata is the static or descriptive information about data assets typically created and assigned during the data creation or documentation. It does not actively monitor, govern, or update the data. Passive metadata includes file names, data creation date, author, file size, and data format.
Passive metadata remains largely static. While it provides basic information about data assets and can aid in data discovery, it doesn't offer real-time insights, data lineage, or automated governance.
On the other hand, active metadata dynamically tracks and manages data throughout its lifecycle.
Active metadata is capable of providing actionable insights without any human intervention. It can flow two ways in the data stack to keep all the data users updated in real-time in the organization. The enriched metadata can be sent across the tools involved in the data management using active metadata management platforms.
Thus, we see organizations moving towards active metadata management from the passive data catalogs of the past.
Prukalpa, the co-founder of Atlan, says:
“We see a fast-growing shift away from traditional data catalogs and toward active metadata management. When data teams begin treating their metadata as an asset, adding automation can enrich and secure data assets, improve data quality, save time, and much more. From identifying, tagging, and securing PII in 5 hours rather than 50 days to saving 40% of a governance team’s time once spent on manual tasks, automation is now an essential part of any modern data team’s toolkit.”
Ease of integration matters to customers
Many active metadata management solution providers offer integration using APIs with various data sources, databases, and data warehouses. G2’s Buyer Behaviour Report also mentions how important ease of integration is to buyers.
84% of buyers want software that can multitask rather than multiple software for solving one concern, the one here being data management.
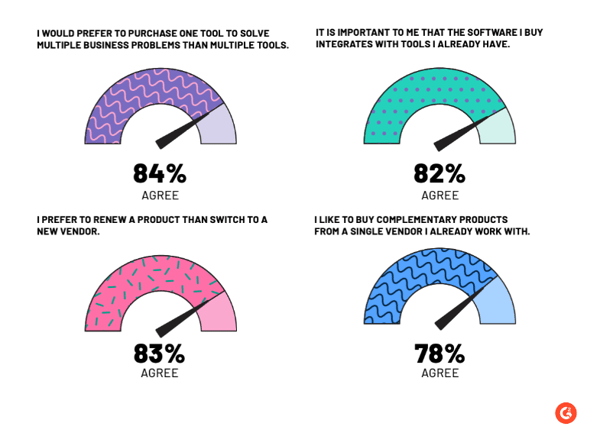 Source: 2023 G2 Software Buyer Behavior Report
Source: 2023 G2 Software Buyer Behavior Report
Standardization in metadata management helps in making the platform interoperable. Thus, the metadata gets easily integrated with various platforms.
Active metadata management is the future of data management
In times of exponential data growth and complexity, active metadata management brings real-time insights, automation, and proactive governance to the forefront.
As data evolves as a strategic asset, active metadata management will be increasingly pivotal in driving efficiency, innovation, and success in the data-driven future.
Explore the comprehensive insights and solutions available in G2's Active Metadata Management category and enhance your data management strategies.
Edited by Shanti S Nair


 by Shalaka Joshi
by Shalaka Joshi
 by Shalaka Joshi
by Shalaka Joshi
 by Shalaka Joshi
by Shalaka Joshi